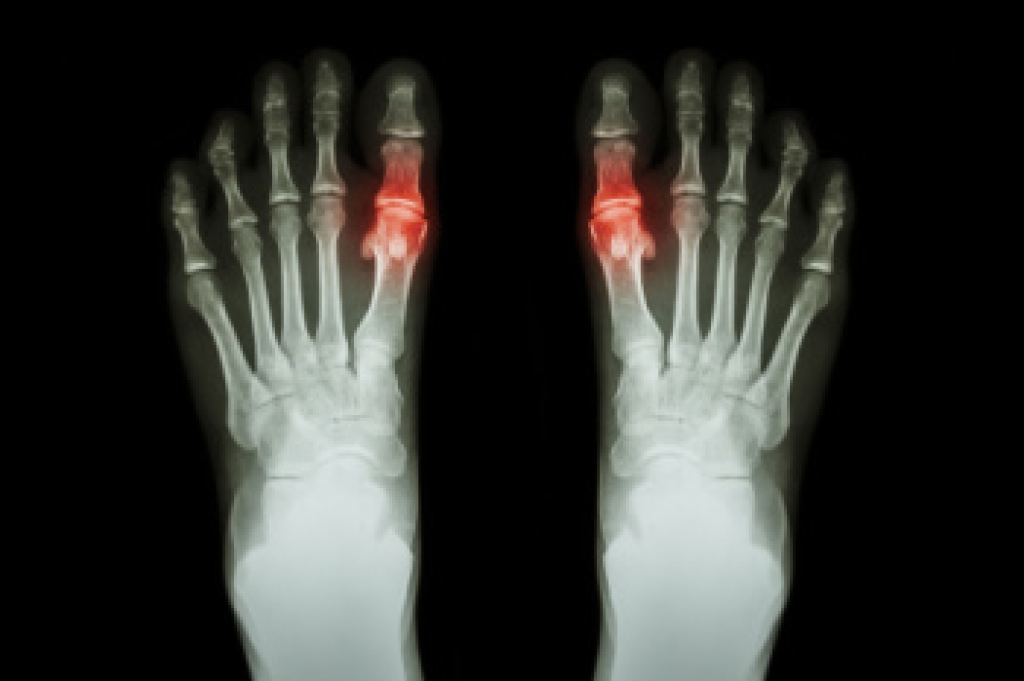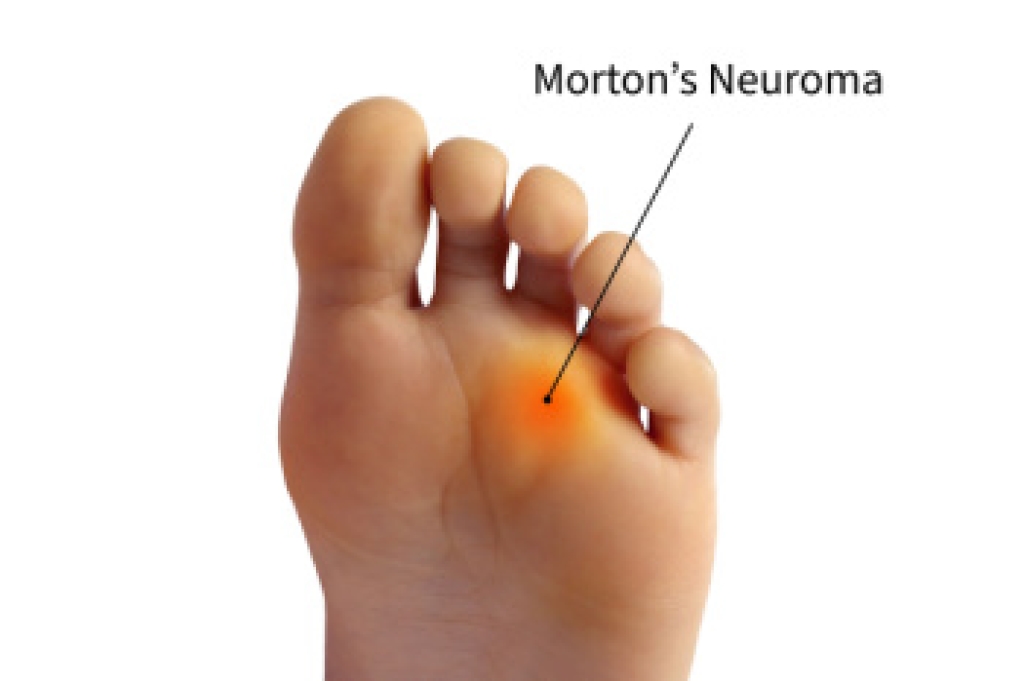
Foot issues, such as plantar fasciitis, heel spurs, and claw toes, can significantly impact daily life. Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the plantar fascia, the thick band of tissue connecting the heel to the toes, causing sharp heel pain, especially in the morning. Heel spurs are bony protrusions that can develop on the heel bone, often linked to plantar fasciitis, leading to persistent pain and discomfort. Claw toes occur when the toe joints bend excessively, resulting in a claw-like appearance. Symptoms include pain, redness, and difficulty wearing shoes comfortably. Experiencing persistent symptoms warrant professional evaluation. A podiatrist might recommend custom orthotics, targeted exercises, or, in some cases, surgery to address the underlying issues. If you are experiencing foot pain or discomfort, it is suggested you schedule an appointment with a podiatrist for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment options, tailored to your needs.
Foot Pain
Foot pain can be extremely painful and debilitating. If you have a foot pain, consult with one of our podiatrists from Greater Boston Foot Care, PLLC. Our doctors will assess your condition and provide you with quality foot and ankle treatment.
Causes
Foot pain is a very broad condition that could be caused by one or more ailments. The most common include:
- Bunions
- Hammertoes
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Bone Spurs
- Corns
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
- Ingrown Toenails
- Arthritis (such as Gout, Rheumatoid, and Osteoarthritis)
- Flat Feet
- Injury (from stress fractures, broken toe, foot, ankle, Achilles tendon ruptures, and sprains)
- And more
Diagnosis
To figure out the cause of foot pain, podiatrists utilize several different methods. This can range from simple visual inspections and sensation tests to X-rays and MRI scans. Prior medical history, family medical history, and any recent physical traumatic events will all be taken into consideration for a proper diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment depends upon the cause of the foot pain. Whether it is resting, staying off the foot, or having surgery; podiatrists have a number of treatment options available for foot pain.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our office located in Plymouth, MA . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.